Shell脚本学习复件
用window7学shell脚本真蛋疼。
Shell有两种执行命令的方式:
* 交互式(Interactive):解释执行用户的命令,用户输入一条命令,Shell就解释执行一条。
* 批处理(Batch):用户事先写一个Shell脚本(Script),其中有很多条命令,让Shell一次把这些命令执行完,而不必一条一条地敲命令。
常见的shell解释器
bash:
可以使用类似DOS下面的doskey的功能,用方向键查阅和快速输入并修改命令。
自动通过查找匹配的方式给出以某字符串开头的命令。
包含了自身的帮助功能,你只要在提示符下面键入help就可以得到相关的帮助。
sh:
sh 是Unix 标准默认的shell
ash:
ash shell 是由Kenneth Almquist编写的,Linux中占用系统资源最少的一个小shell,它只包含24个内部命令,因而使用起来很不方便。
csh:
csh 是Linux比较大的内核,它由以William Joy为代表的共计47位作者编成,共有52个内部命令。该shell其实是指向/bin/tcsh这样的一个shell,也就是说,csh其实就是tcsh。
ksh
ksh 是Korn shell的缩写,由Eric Gisin编写,共有42条内部命令。该shell最大的优点是几乎和商业发行版的ksh完全兼容,这样就可以在不用花钱购买商业版本的情况下尝试商业版本的性能了
编译型语言:
这类语言需要预先将我们写好的源代码(source code)转换成目标代码(object code),这个过程被称作“编译”。
解释型语言:
解释型语言也被称作“脚本语言”。执行这类程序时,解释器(interpreter)需要读取我们编写的源代码(source code),并将其转换成目标代码(object code),再由计算机运行。
什么情况下使用,什么情况下不适用?
优点:
简单性:Shell是一个高级语言;通过它,你可以简洁地表达复杂的操作。
可移植性:使用POSIX所定义的功能,可以做到脚本无须修改就可在不同的系统上执行。
开发容易:可以在短时间内完成一个功能强大又妤用的脚本。
缺点:
资源密集型的任务,尤其在需要考虑效率时(比如,排序,hash等等)。
需要处理大任务的数学操作,尤其是浮点运算,精确运算,或者复杂的算术运算(这种情况一般使用C++或FORTRAN 来处理)。
有跨平台(操作系统)移植需求(一般使用C 或Java)。
复杂的应用,在必须使用结构化编程的时候(需要变量的类型检查,函数原型,等等)。
对于影响系统全局性的关键任务应用。
对于安全有很高要求的任务,比如你需要一个健壮的系统来防止入侵、破解、恶意破坏等等。
项目由连串的依赖的各个部分组成。
需要大规模的文件操作。
需要多维数组的支持。
需要数据结构的支持,比如链表或数等数据结构。
需要产生或操作图形化界面 GUI。
需要直接操作系统硬件。
需要 I/O 或socket 接口。
需要使用库或者遗留下来的老代码的接口。
私人的、闭源的应用(shell 脚本把代码就放在文本文件中,全世界都能看到)。
创建文件
touch testShell.sh
Shell变量:Shell变量的定义、删除变量、只读变量、变量类型
变量名的命名须遵循如下规则:
首个字符必须为字母(a-z,A-Z)。
中间不能有空格,可以使用下划线(_)。
不能使用标点符号。
不能使用bash里的关键字(可用help命令查看保留关键字)。
myUrl="http://see.xidian.edu.cn/cpp/linux/"
myNum=100
使用变量
使用一个定义过的变量,只要在变量名前面加美元符号($)即可

只读变量
使用 readonly 命令可以将变量定义为只读变量,只读变量的值不能被改变。
#!/bin/bashmyUrl="http://see.xidian.edu.cn/cpp/shell/"readonly myUrlmyUrl="http://see.xidian.edu.cn/cpp/danpianji/"
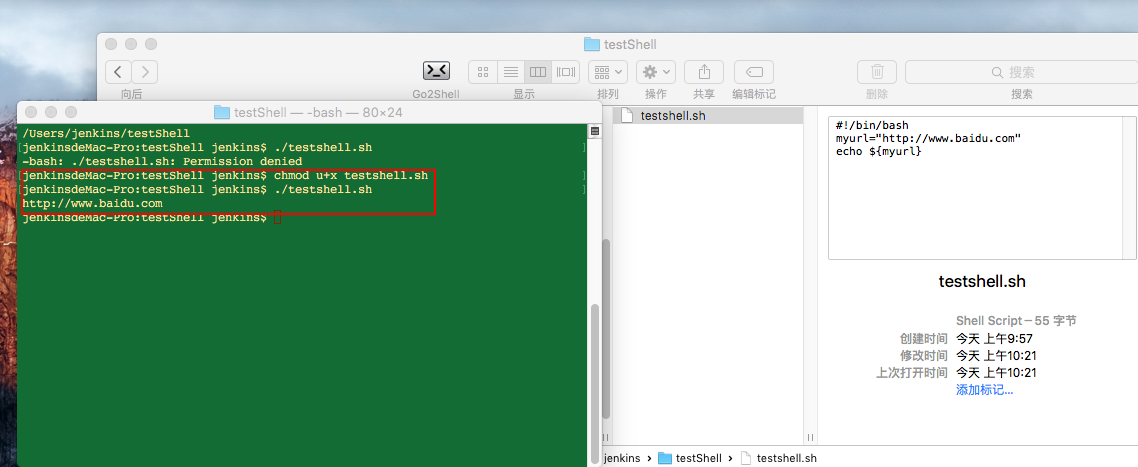
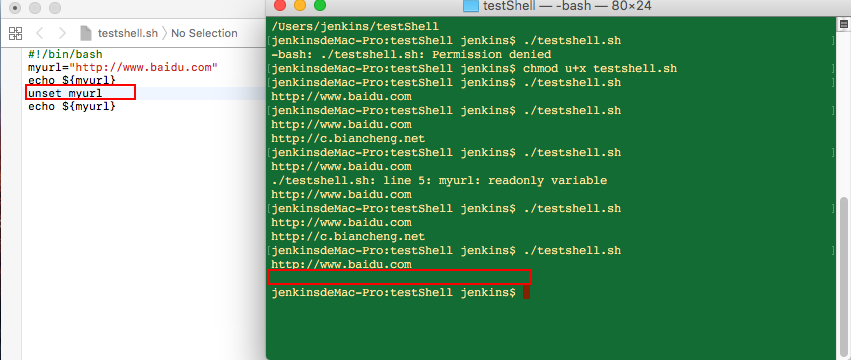
执行.sh文件里面的内容:
#!/bin/bashmyurl="http://www.baidu.com"echo ${myurl} 看下效果:
重新定义变量
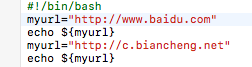
运行结果:

删除变量
使用 unset 命令可以删除变量。语法:
纯文本复制
unset variable_name
示例demo可见结果中第二行没有内容显示,删除成功
变量类型
运行shell时,会同时存在三种变量:
1) 局部变量
局部变量在脚本或命令中定义,仅在当前shell实例中有效,其他shell启动的程序不能访问局部变量。
2) 环境变量
所有的程序,包括shell启动的程序,都能访问环境变量,有些程序需要环境变量来保证其正常运行。必要的时候shell脚本也可以定义环境变量。
3) shell变量
shell变量是由shell程序设置的特殊变量。shell变量中有一部分是环境变量,有一部分是局部变量,这些变量保证了shell的正常运行
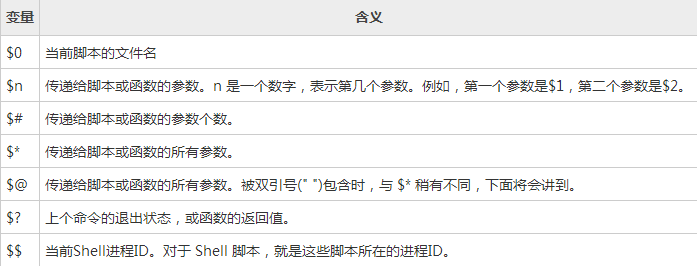
Shell特殊变量:Shell $0, $#, $*, $@, $?, $$和命令行参数
Shell替换:Shell变量替换,命令替换,转义字符
-e 表示对转义字符进行替换。如果不使用 -e 选项,将会原样输出
#!/bin/basha=10echo -e "Value of a is $a \n"

命令替换
命令替换是指Shell可以先执行命令,将输出结果暂时保存,在适当的地方输出:
#!/bin/bashDATE=`date`echo "Date is $DATE"USERS=`who | wc -l`echo "Logged in user are $USERS"UP=`date ; uptime`echo "Uptime is $UP"
执行结果:
$ ./test.shDate is 2017年04月12日 10:20:51Logged in user are 0./test.sh: line 6: uptime: command not foundUptime is 2017年04月12日 10:20:51
变量替换

变量替换可以根据变量的状态(是否为空、是否定义等)来改变它的值
#!/bin/bash echo ${var:-"Variable is not set"}echo "1 - Value of var is ${var}" echo ${var:="Variable is not set"}echo "2 - Value of var is ${var}" unset varecho ${var:+"This is default value"}echo "3 - Value of var is $var" var="Prefix"echo ${var:+"This is default value"}echo "4 - Value of var is $var" echo ${var:?"Print this message"}echo "5 - Value of var is ${var}"执行结果: $ ./test.shVariable is not set1 - Value of var isVariable is not set2 - Value of var is Variable is not set 3 - Value of var isThis is default value4 - Value of var is PrefixPrefix5 - Value of var is Prefix Shell运算符:Shell算数运算符、关系运算符、布尔运算符、字符串运算符等
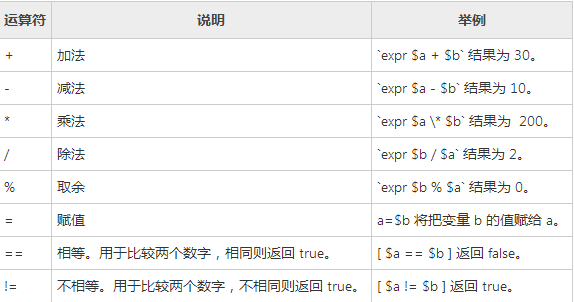
Shell算数运算符:
#!/bin/sh a=101b=225#加val=`expr $a + $b`echo "a + b : $val"#减val=`expr $a - $b`echo "a - b : $val"#程val=`expr $a \* $b`echo "a * b : $val"#除val=`expr $b / $a`echo "b / a : $val"#求余val=`expr $b % $a`echo "b % a : $val" if [ $a == $b ]then echo "a is equal to b"fi if [ $a != $b ]then echo "a is not equal to b"fi
结果:
$ ./test.sha + b : 326a - b : -124a * b : 22725b / a : 2b % a : 23a is not equal to b
关系运算符
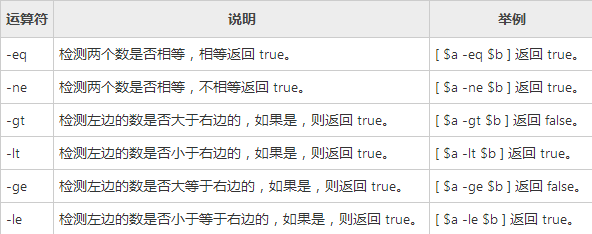
关系运算符只支持数字,不支持字符串,除非字符串的值是数字。
#!/bin/sh a=10b=20#检测两个数是否相等,相等返回 true。if [ $a -eq $b ]then echo "$a -eq $b : a is equal to b"else echo "$a -eq $b: a is not equal to b"fi #检测两个数是否相等,不相等返回 true。if [ $a -ne $b ]then echo "$a -ne $b: a is not equal to b"else echo "$a -ne $b : a is equal to b"fi #检测左边的数是否大于右边的,如果是,则返回 true。if [ $a -gt $b ]then echo "$a -gt $b: a is greater than b"else echo "$a -gt $b: a is not greater than b"fi #检测左边的数是否小于右边的,如果是,则返回 true。if [ $a -lt $b ]then echo "$a -lt $b: a is less than b"else echo "$a -lt $b: a is not less than b"fi #检测左边的数是否大等于右边的,如果是,则返回 true。if [ $a -ge $b ]then echo "$a -ge $b: a is greater or equal to b"else echo "$a -ge $b: a is not greater or equal to b"fi #检测左边的数是否小于等于右边的,如果是,则返回 true。if [ $a -le $b ]then echo "$a -le $b: a is less or equal to b"else echo "$a -le $b: a is not less or equal to b"fi
结果:
Administrator@XY9A6SI917CWQBC MINGW32 /h$ ./test.sh10 -eq 20: a is not equal to b10 -ne 20: a is not equal to b10 -gt 20: a is not greater than b10 -lt 20: a is less than b10 -ge 20: a is not greater or equal to b10 -le 20: a is less or equal to b
布尔运算符
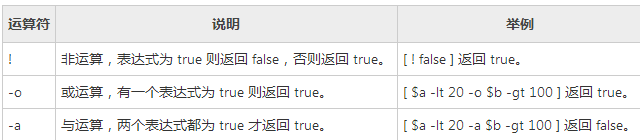
示例:
#!/bin/sh a=10b=20#非运算,表达式为 true 则返回 false,否则返回 trueif [ $a != $b ]then echo "$a != $b : a is not equal to b"else echo "$a != $b: a is equal to b"fi#与运算,两个表达式都为 true 才返回 true。if [ $a -lt 100 -a $b -gt 15 ]then echo "$a -lt 100 -a $b -gt 15 : returns true"else echo "$a -lt 100 -a $b -gt 15 : returns false"fi#或运算,有一个表达式为 true 则返回 true。if [ $a -lt 100 -o $b -gt 100 ]then echo "$a -lt 100 -o $b -gt 100 : returns true"else echo "$a -lt 100 -o $b -gt 100 : returns false"fi#或运算,有一个表达式为 true 则返回 true。if [ $a -lt 5 -o $b -gt 100 ]then echo "$a -lt 100 -o $b -gt 100 : returns true"else echo "$a -lt 100 -o $b -gt 100 : returns false"fi
结果:
Administrator@XY9A6SI917CWQBC MINGW32 /h$ ./test.sh10 != 20 : a is not equal to b10 -lt 100 -a 20 -gt 15 : returns true10 -lt 100 -o 20 -gt 100 : returns true10 -lt 100 -o 20 -gt 100 : returns false
字符串运算符

示例demo:
#!/bin/sh a="abc"b="efg" #= 检测两个字符串是否相等,相等返回 true。 [ $a = $b ] 返回 false。if [ $a = $b ]then echo "$a = $b : a is equal to b"else echo "$a = $b: a is not equal to b"fi #!= 检测两个字符串是否相等,不相等返回 true。 [ $a != $b ] 返回 true。if [ $a != $b ]then echo "$a != $b : a is not equal to b"else echo "$a != $b: a is equal to b"fi #-z 检测字符串长度是否为0,为0返回 true。 [ -z $a ] 返回 false。if [ -z $a ]then echo "-z $a : string length is zero"else echo "-z $a : string length is not zero"fi #-n 检测字符串长度是否为0,不为0返回 true。 [ -n $a ] 返回 true。if [ -n $a ]then echo "-n $a : string length is not zero"else echo "-n $a : string length is zero"fi #str 检测字符串是否为空,不为空返回 true。 [ $a ] 返回 true。if [ $a ]then echo "$a : string is not empty"else echo "$a : string is empty"fi
结果:
Administrator@XY9A6SI917CWQBC MINGW32 /h$ ./test.shabc = efg: a is not equal to babc != efg : a is not equal to b-z abc : string length is not zero-n abc : string length is not zeroabc : string is not empty
文件测试运算符
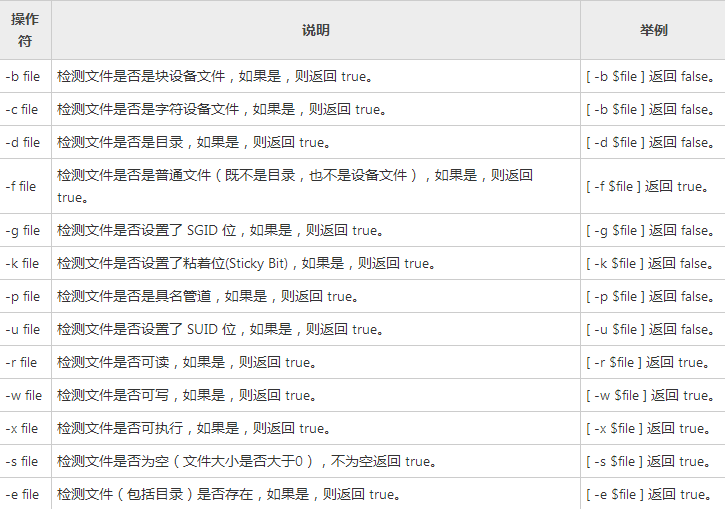
文件:
代码示例:#!/bin/sh file="H:/test.sh" #-r file 检测文件是否可读,如果是,则返回 true。 [ -r $file ] 返回 true。if [ -r $file ]then echo "File has read access"else echo "File does not have read access"fi #-w file 检测文件是否可写,如果是,则返回 true。 [ -w $file ] 返回 true。if [ -w $file ]then echo "File has write permission"else echo "File does not have write permission"fi #-x file 检测文件是否可执行,如果是,则返回 true。 [ -x $file ] 返回 true。if [ -x $file ]then echo "File has execute permission"else echo "File does not have execute permission"fi #-f file 检测文件是否是普通文件(既不是目录,也不是设备文件),如果是,则返回 true。 [ -f $file ] 返回 true。if [ -f $file ]then echo "File is an ordinary file"else echo "This is sepcial file"fi #-d file 检测文件是否是目录,如果是,则返回 true。 [ -d $file ] 返回 false。if [ -d $file ]then echo "File is a directory"else echo "This is not a directory"fi #-s file 检测文件是否为空(文件大小是否大于0),不为空返回 true。 [ -s $file ] 返回 true。if [ -s $file ]then echo "File size is zero"else echo "File size is not zero"fi#-e file 检测文件(包括目录)是否存在,如果是,则返回 true。 [ -e $file ] 返回 true。if [ -e $file ]then echo "File exists"else echo "File does not exist"fi
结果:
Administrator@XY9A6SI917CWQBC MINGW32 /h$ ./test.shFile has read accessFile has write permissionFile has execute permissionFile is an ordinary fileThis is not a directoryFile size is zeroFile exists
注释
单行注释
#
多行注释
直接
{
}
花括号括起来,不去调用就行
Shell字符串
单引号:
str='this is a string'
单引号字符串的限制:
单引号里的任何字符都会原样输出,单引号字符串中的变量是无效的;
单引号字串中不能出现单引号(对单引号使用转义符后也不行)。
双引号:
your_name='qinjx'str="Hello, I know your are \"$your_name\"! \n"
双引号的优点:
双引号里可以有变量
双引号里可以出现转义字符
拼接字符串
your_name="qinjx"greeting="hello, "$your_name" !"greeting_1="hello, ${your_name} !"echo $greeting $greeting_1 结果:
$ ./test.shhello, qinjx ! hello, qinjx !
获取字符串长度
string="abcd"echo ${#string} #输出 4 结果:
$ ./test.sh4
提取子字符串
纯文本复制
string="alibaba is a great company"echo ${ string:1:4} #输出liba 结果:
$ ./test.shliba
查找子字符串
string="alibaba is a great company"echo `expr index "$string" is`
结果:
$ ./test.sh3
定义数组
在Shell中,用括号来表示数组,数组元素用“空格”符号分割开。定义数组的一般形式为:
array_name=(value1 ... valuen) array_name=(value0 value1 value2 value3)
或
array_name=( value0 value1 value2 value3 )
或
array_name[0]=value0 array_name[1]=value1 array_name[2]=value2
读取数组
读取数组元素值的一般格式是:
${array_name[index]} valuen=${array_name[2]} 例如:
#!/bin/shNAME[0]="张三"NAME[1]="李四"NAME[2]="王麻子"NAME[3]="赵六"NAME[4]="程起"echo "First Index: ${NAME[0]}"echo "Second Index: ${NAME[1]}" 结果:
$ ./test.shFirst Index: 张三Second Index: 李四
使用@ 或 * 可以获取数组中的所有元素
#!/bin/shNAME[0]="张三"NAME[1]="李四"NAME[2]="王麻子"NAME[3]="赵六"NAME[4]="程起"echo "First Index: ${NAME[0]}"echo "Second Index: ${NAME[1]}"#使用@ 或 * 可以获取数组中的所有元素echo "All : ${NAME[@]}"echo "All : ${NAME[*]}" 结果:
$ ./test.shFirst Index: 张三Second Index: 李四All : 张三 李四 王麻子 赵六 程起All : 张三 李四 王麻子 赵六 程起
获取数组的长度
获取数组长度的方法与获取字符串长度的方法相同。
# 取得数组元素的个数length=${#array_name[@]}# 或者length=${#array_name[*]}# 取得数组单个元素的长度lengthn=${#array_name[n]} 例如:
#!/bin/shNAME[0]="张三"NAME[1]="李四"NAME[2]="王麻子"NAME[3]="赵六"NAME[4]="程起"echo "First Index: ${NAME[0]}"echo "Second Index: ${NAME[1]}"#使用@ 或 * 可以获取数组中的所有元素echo "All : ${NAME[@]}"echo "All : ${NAME[*]}"echo "${#NAME[@]}"echo "${#NAME[*]}"echo "${#NAME[n]}" 结果:
$ ./test.shFirst Index: 张三Second Index: 李四All : 张三 李四 王麻子 赵六 程起All : 张三 李四 王麻子 赵六 程起552
Shell echo命令
echo是Shell的一个内部指令,用于在屏幕上打印出指定的字符串:
echo arg
您可以使用echo实现更复杂的输出格式控制。
显示转义字符
echo "\"It is a test\""
结果将是:
"It is a test"
双引号也可以省略。
显示变量
name="OK"echo "$name It is a test"
结果将是:
OK It is a test
同样双引号也可以省略。
如果变量与其它字符相连的话,需要使用大括号({ }):
mouth=8echo "${mouth}-1-2009" 结果将是:
8-1-2009
显示换行
echo "OK!\n"echo "It is a test"
输出:
$ ./test.shOK!It is a test
显示不换行
echo "OK!\c"echo "It is a test"
输出:
OK!It si a test
显示结果重定向至文件
echo "It is a test" > myfile
原样输出字符串
$ ./test.sh
若需要原样输出字符串(不进行转义),请使用单引号。例如:
echo '$name\"'
显示命令执行结果
echo `date`
结果将显示当前日期
$ ./test.sh2017年04月13日 14:00:47
shell printf命令:格式化输出语句
printf 命令用于格式化输出, 是echo命令的增强版。
Shell if else语句
if ... fi 语句;if ... else ... fi 语句;if ... elif ... else ... fi 语句。 if else语法: if [条件]then条件为true执行语句fi
例如:
#!/bin/sha=88b=105if [ $a == $b ]then echo "a is equal to b"fiif [ $a != $b ]then echo "a is not equal to b"fi
结果:
$ ./test.sha is not equal to b
if ... else ... fi 语句
语法:
if [ 条件 ]then 条件为trueelse 条件为falsefi
demo:
#!/bin/sha=88b=105if [ $a == $b ]then echo "a is equal to b"else echo "a is not equal to b"fi
结果:
$ ./test.sha is not equal to b
if ... elif ... fi 语句
语法:
if [ 条件 1 ]then 条件1成立elif [ 条件 2 ]then 条件2成立elif [ 条件 3 ]then 条件3成立else 条件1,2,3都不成立的情况下执行fi
示例:
#!/bin/sha=88b=105 if [ $a == $b ]then echo "a 等于 b"elif [ $a -gt $b ]then echo "a 大于 b"elif [ $a -lt $b ]then echo "a 小于 b"else echo "上面条件都不满足"fi
结果:
$ ./test.sha 小于 b
还有两种方式:
第一种:
#!/bin/shif test $[3*3] -eq $[4+5]; then echo 'The two numbers are equal!'; fi;
结果:
$ ./test.shThe two numbers are equal!
第二种:
#!/bin/shnum1=$[3*3]num2=$[4+5]if test $[num1] -eq $[num2]then echo 'The two numbers are equal!'else echo 'The two numbers are not equal!'fi
结果:
$ ./test.shThe two numbers are equal!
Shell case esac语句
相当于java的switch case语句
语法:
case 要判断的内容 in值1) 要判断的内容等于值1 ;;模式2) 要判断的内容等于值2 ;;*) 不等于值1,也不等于值2 ;;esac
demo:
#!/bin/bash echo "Input a number between 1 to 4"echo -e "Your number is:\c"read aNumcase ${aNum} in1) echo "You select 1";;2) echo "You select 2";;3) echo "You select 3";;4) echo "You select 4";;*) echo "You do not select a number between 1 to 4";;esac 结果:
$ ./test.shInput a number between 1 to 4Your number is:2You select 2
循环语句:
demo:
#!/bin/bash for loop in 1 2 3 4 5do echo "The value is: $loop"done
结果:
$ ./test.shThe value is: 1The value is: 2The value is: 3The value is: 4The value is: 5
Shell while循环:
语法:
while 条件do 满足条件,循环语句done
例子:
#! /bin/bashdeclare -i COUNTER=0while [ $COUNTER -lt 5 ]doCOUNTER=`expr $COUNTER+1`echo $COUNTERdone
COUNTER小于5不断循环直到大于等于5才退出
$ ./test.sh12345
Shell until循环
语法:
until 条件为falsedo 条件为false执行循环语句,否则跳出循环done
例如:
#!/bin/basha=0until [ ! $a -lt 10 ]do echo $a a=`expr $a + 1`done
结果:当a = 10的时候 ,! $a -lt 10为true跳出循环
$ ./test.sh0123456789
Shell break和continue命令
break命令
break命令允许跳出所有循环(终止执行后面的所有循环)
#!/bin/basha=0while [ $a -lt 1 ]do echo -n "Input a number between 1 to 5: " read aNum case $aNum in 1|2|3|4|5) echo "Your number is $aNum!" ;; *) echo "You do not select a number between 1 to 5, game is over!" break ;; esacdone
首先外面是死循环,不断让你输入,如果输入内容在1到5之间,就输出:your number is 你输入的值,如果大于不在这个之间就会输出"You do not select a number between 1 to 5, game is over! "并且跳出循环语句。
看下结果:
$ ./test.shInput a number between 1 to 5: 1Your number is 1!Input a number between 1 to 5: 2Your number is 2!Input a number between 1 to 5: 3Your number is 3!Input a number between 1 to 5: 4Your number is 4!Input a number between 1 to 5: 5Your number is 5!Input a number between 1 to 5: 6You do not select a number between 1 to 5, game is over!
demo2:
#!/bin/bash for var1 in 1 2 3do for var2 in 0 5 do if [ $var1 -eq 2 -a $var2 -eq 0 ] then break 2 else echo "$var1 $var2" fi done
当var1 = 2 ,var2 =0 的时候 跳出循环,因此只可能有1,0 ;2,5
continue命令
continue命令与break命令类似,只有一点差别,它不会跳出所有循环,仅仅跳出当前循环。
#!/bin/bashwhile :do echo -n "Input a number between 1 to 5: " read aNum case $aNum in 1|2|3|4|5) echo "Your number is $aNum!" ;; *) echo "You do not select a number between 1 to 5!" continue echo "Game is over!" ;; esacdone
结果:
$ ./test.shInput a number between 1 to 5: 1Your number is 1!Input a number between 1 to 5: 2Your number is 2!Input a number between 1 to 5: 3Your number is 3!Input a number between 1 to 5: 4Your number is 4!Input a number between 1 to 5: 5Your number is 5!Input a number between 1 to 5: 6You do not select a number between 1 to 5!Input a number between 1 to 5: 7You do not select a number between 1 to 5!Input a number between 1 to 5:
因为continue会跳出本次循环,所以永远不会执行:echo "Game is over!"
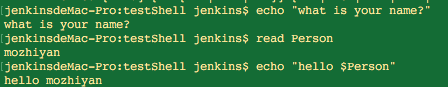
Shell函数:Shell函数返回值、删除函数、在终端调用函数
1 无返回值的函数方法:
#!/bin/bash# Define your function hereHello () { echo "Url is http://see.xidian.edu.cn/cpp/shell/"}# Invoke your functionHello 结果:
$ ./test.shUrl is http://see.xidian.edu.cn/cpp/shell/
有返回值的函数:
#!/bin/bashfunWithReturn(){ echo "该方法获取输入内容总和" echo -n "值1:" read aNum echo -n "值2:" read anotherNum return $(($aNum+$anotherNum))}funWithReturn# 调用并返回的值ret=$?echo "两数之和是 $ret !" 结果:
$ ./test.sh该方法获取输入内容?和 值?1Ʌ2„值?
函数嵌套:
#!/bin/bash# Calling one function from anothernumber_one () { echo "Url_1 is http://c.biancheng.net/cpp/view/2491.html" number_two}number_two () { echo "Url_2 is http://192.168.30.7:8090/pages/viewpage.action?pageId=12387047"}number_one 结果:
$ ./test.shUrl_1 is http://c.biancheng.net/cpp/view/2491.htmlUrl_2 is http://192.168.30.7:8090/pages/viewpage.action?pageId=12387047
Shell文件包含
文件1
test.sh里面内容:
#!/bin/bash. ./test2.shecho $url
test2.sh里面的内容:
url="https://juejin.im/timeline/android"
执行:
$ ./test.shhttps://juejin.im/timeline/android
Shell输入输出重定向:Shell Here Document,/dev/null文件
输出重定向
命令的输出不仅可以是显示器,还可以很容易的转移向到文件,这被称为输出重定向。
bash界面输入:
$ fileUsage: file [-bcEhikLlNnprsvzZ0] [--apple] [--extension] [--mime-encoding] [--mime-type] [-e testname] [-F separator] [-f namefile] [-m magicfiles] file ... file -C [-m magicfiles] file [--help]
首先看下文件:
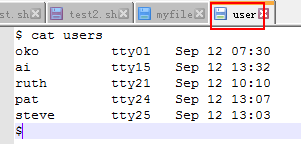
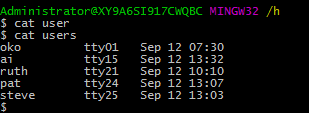
然后shell命令:
cat user